Finding the Perfect Volleyball Position
Volleyball demands a variety of skills and personal characteristics. The specific position a player holds is shaped by their physique, agility, endurance, and overall volleyball proficiency. Skill development through steady, focused practice enables players to perform well across different roles.
Crucial skills such as serving, blocking, setting, hitting, and digging are vital for success in the game. Often, the skill that a player masters first may signal the most fitting position for them, as each requires distinct capabilities and expertise.
Key Volleyball Positions Explained
- Outside Hitter
An outside hitter, also known as a left-side hitter, operates from both the front and back rows on the left side. Their primary role involves attacking and passing, handling a majority of the sets during a game. They must excel in converting even challenging passes into successful attacks and contribute effectively in serving and defending when positioned in the back row. - Middle Blocker
Positioned in the center of the front row, the middle blocker focuses on blocking and attacking. This player is pivotal in executing quick hits and effective blocks, especially under optimal set conditions. They often rotate out for a libero in the back row, depending on team strategy and individual skills. - Opposite Hitter
Known as the opposite, this player covers the right side of the court in both the front and back rows. Their responsibilities include blocking and attacking, particularly against opposing outside hitters. The opposite is crucial in plays, particularly at higher levels where setting across the court becomes more common. - Setter
The setter is key to volleyball strategy, responsible for orchestrating the offense by setting the ball for attacks. While primarily setting from the right side, their position can vary based on the team’s dynamic and the game plan, playing in both the front and back rows as needed. - Libero
Distinguished by a different colored jersey, the libero specializes in defensive plays from the back row, particularly in serve receive and general defense. They also serve as an alternate setter when required. Rules regarding libero rotations and substitutions vary by league, but they are essential for maintaining strong back-row defense. - Defensive Specialist (DS)
A defensive specialist is primarily substituted in to bolster the team’s defense, particularly in serve receive situations. Their role is to enhance the team’s defensive continuity and can be strategically subbed in based on the flow of the game and player performance. - Serving Specialist
This player, a serving specialist, enters the game solely to serve, maximizing the team’s serving strategy. Their participation is typically brief, focused on serving until the next side out, after which they are usually substituted out depending on the game’s needs and player skills.

Volleyball Court Dimensions and Specifications
Playing Area
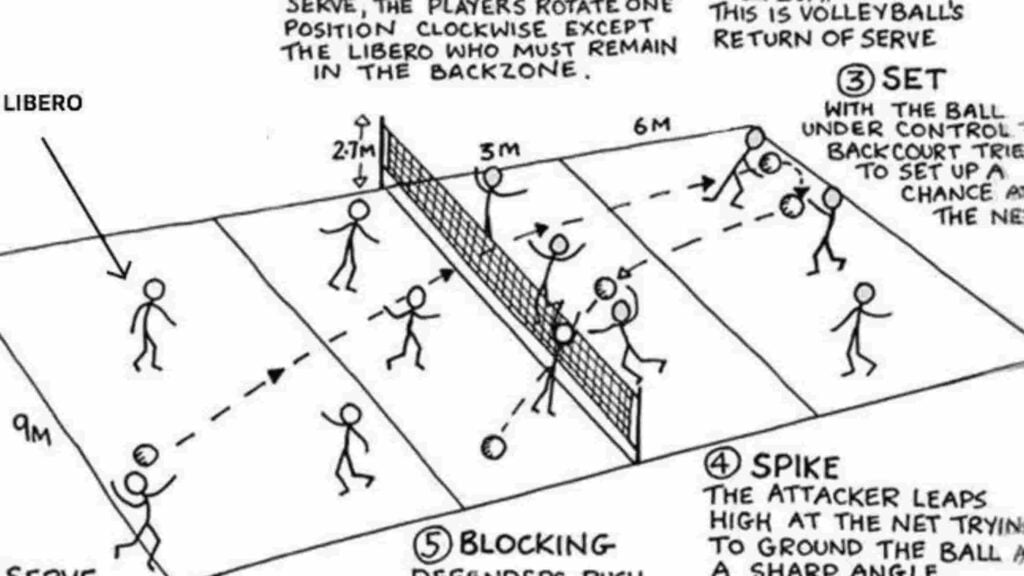
A regulation volleyball court measures 18 meters by 9 meters. To facilitate gameplay, including serving and safe movement for players to retrieve off-target passes, the court is set within a larger area. This space also accommodates referees and other game officials.
Net Height
The height of the volleyball net varies based on the game format. For standard competitive matches, the net is set at 2.43 meters for men and 2.24 meters for women, ensuring appropriate gameplay dynamics for each category.
Read Also: 5-1 Volleyball Rotation [Top Strategies]
Key Elements of Volleyball Scoring and Regulations
Scoring Overview
Volleyball embraced the rally scoring system in 1998, enabling both teams to score points during a rally, irrespective of which team served. This change enhances the game’s pace and competitiveness. Regular matches are divided into up to five sets, with the first four sets aiming for 25 points each and the fifth, if necessary, capped at 15 points. A team must secure a two-point lead to win a set, potentially leading to extended play in tightly contested matches.
Game Rules
Volleyball England, the governing body for the sport within England, defines an official game court as 18 meters long and 9 meters wide. Games initiate with a serve from behind the end line, and players may use either an overarm or underarm technique. Teams are allowed a maximum of three touches to return the ball over the net, with consecutive touches by the same player prohibited. The aim is to hit rather than catch the ball. Sideout scoring is applied when the opposing team fails to return the ball, sends it out of bounds, or breaches other game rules.
Roles of Officials
A complete officiating crew includes a first referee, a second referee, a scorer, and two to four line judges. The first referee has the final say on all rulings during the match and records any formal protests with the help of the scorer. The second referee handles substitutions, timeouts, and oversees the scorer’s table. Line judges, akin to their roles in tennis, ensure the accuracy of boundary and line-related decisions.
This straightforward explanation details the primary aspects of volleyball’s scoring system, rules, and official roles, making it accessible for individuals as young as teenagers to comprehend.
FAQ’s: Volleyball Position
What is the most crucial Volleyball Position?
The setter is essential in volleyball, primarily responsible for the offense. They need to set the ball accurately for attackers and excel in communication to coordinate the team’s efforts efficiently.
What is the rarest position in volleyball?
The middle blocker position is notably the least common. Finding skilled middle blockers who can effectively read and react during plays is challenging. While it may be easier to train someone to attack from the middle, the defensive capabilities are what distinguish exceptional middle blockers.
Who serves in a volleyball position?
In volleyball, the player in Position 1, located in the back-right section of the court, serves. Players rotate to this position in a clockwise manner, and when it’s their turn, they can serve from anywhere behind the end line.
How do players rotate in volleyball?
In volleyball, players rotate clockwise every time their team gains possession of the serve. The rotation moves the left front player to the middle front, the middle front to the right front, and continues in this pattern. The player moving into the right-back position becomes responsible for serving.
What is the purpose of different volleyball positions?
In volleyball, each position has a specialized role: The setter (S) coordinates the offense by managing the second touch and setting up attacks. The libero (L) is a defensive specialist, known for quick reflexes and agility. Outside hitters (OH) handle a mix of passing, attacking, and serving. Opposite hitters (Opp or RS) focus on scoring, serving, and blocking, playing a critical role in both offense and defense.





